News Archive
Filter by Division
Filter by Categories
Researchers identify factor that drives prostate cancer-causing genes
September 10, 2024 / Cancer ResearchResearchers at the University of Michigan Health Rogel Cancer Center have uncovered a key reason why a typically normal protein goes awry and fuels cancer.
They found the protein NSD2 alters the function of the androgen receptor, an important regulator of normal prostate development. When androgen receptor binds with NSD2, it causes rapid cell division and growth leading to prostate cancer. The study, published in Nature Genetics, may suggest a new way to therapeutically target prostate cancer. The findings illuminate a phenomenon not previously understood.
Researchers find common immune system mechanism between pregnancy, cancer
July 8, 2024 / FacultyTo understand why some cancers successfully circumvent the immune system to grow unchecked, researchers turned to pregnancy.
 “In pregnancy, the immune system does not reject the growing fetus, so we know there must be mechanisms active in the placenta. In cancer, it’s the same thing: the growing tumor is not rejected by the immune system. It means the cancer cells have developed strategies to suppress immune rejection, same as in pregnancy,” said Weiping Zou, M.D., Ph.D., professor of experimental pathology.
“In pregnancy, the immune system does not reject the growing fetus, so we know there must be mechanisms active in the placenta. In cancer, it’s the same thing: the growing tumor is not rejected by the immune system. It means the cancer cells have developed strategies to suppress immune rejection, same as in pregnancy,” said Weiping Zou, M.D., Ph.D., professor of experimental pathology.
It’s a good thing in pregnancy – it allows the baby to grow. But in cancer, it means the tumor grows unchecked and treatments meant to stimulate an immune response are not effective.
Dr. Analisa DiFeo named 2024 Rogel Scholar
July 3, 2024 / Cancer ResearchDepartment of Pathology faculty member, Analisa DiFeo, PhD, has been named a 2024 Rogel Scholar by Michigan Medicine. The award supports exceptional faculty dedicated to achieving impact on cancer prevention, patient outcomes, and quality of life. Please join us in congratulating Dr. Analisa DiFeo on this prestigious award!
With $5M Grant, Rogel Team Will Conduct Preclinical Work to Develop Drugs Targeting Cancer Master Regulator
May 8, 2024 / MctpUniversity of Michigan Rogel Cancer Center researcher Arul Chinnaiyan, MD, PhD, has received a $5 million grant from the J.C. Kennedy Foundation to conduct laboratory tests of a potential drug candidate targeting a master regulator that controls the majority of genes involved in the most challenging type of prostate cancer. The SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complex was previously found to facilitate access to enhancers that oncogenes can bind to, driving downstream gene expression in cancer. Degrading a subunit of this complex blocks the oncogenes [...]
Rogel Researchers Receive $4M Through Prostate Cancer Foundations Inaugural TACTICAL Awards Program
January 10, 2023 / MctpThe University of Michigan Rogel Cancer Center researchers received one of the Prostate Cancer Foundation’s four inaugural Class of 2022 TACTICAL (Therapy ACceleration To Intercept Cancer Lethality) Award. This $30 million program will support cross-disciplinary pioneering research toward the goal of developing 21st Century therapies for the most life-threatening form of prostate cancer [...]
Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma study results published
January 6, 2023 / Experimental PathologyMembers of the University of Michigan Department of Pathology and Michigan Center for Translational Pathology, in collaboration with the Clinical Proteomic Tumor Analysis Consortium, recently published a large study on clear cell renal cell carcinomas (ccRCCs), which represent about 75% of the RCC cases and account for the most RCC-associated deaths. This study set out to create a comprehensive profile of ccRCC, combining histologic and molecular profiles. By analyzing both the microscopic cell structures and the genetic makeup of the cells, these researchers discovered significant intratumoral heterogeneity in 90% of ccRCCs. This indicates that ccRCCs originate from multiple tumor cell lines, called tumor subclones, that may become metastatic and could independently influence response to therapies. Through this study, the team was able to molecularly stratify aggressive histopathic subtypes, which may lead to more effective treatment strategies for patients and improved survival.
A new cooperation between EZH2 and p38 proteins enhances metastasis in triple negative breast cancer
August 17, 2022 / Experimental PathologyThe Celina Kleer lab at the University of Michigan Department of Pathology and Rogel Cancer Center has found a new mechanism that fuels metastasis in triple negative breast cancers. In their new study they show that EZH2, a master regulator of cell type identity, known to function through methylation of histones, has a new, unexpected function in aggressive breast cancers [...]
Researchers Find Link Between Genetic Mutations and Cancer Treatment Resistance
July 26, 2022 / MctpPatients with relapsed multiple myeloma are resistant to commonly used treatments. Researchers are one step closer to understanding the genetic reason why.
TRIM63 - What is it? (Hint: Not a weight-loss product)
August 9, 2021 / CancerDr. Xiao-Ming (Mindy) Wang and colleagues from the Michigan Center for Translational Pathology and Department of Pathology published a groundbreaking finding from an inter-institutional study regarding TRIM63 in Modern Pathology [...]
Researchers Uncover Way to Harness the Power of Immunotherapy for Advanced Prostate Cancer
August 3, 2021 / BlogFindings offer clues to why some types of renal cell carcinoma respond to immunotherapy while others do not — it’s a scientific riddle tangled up in a complex web. How do you turn an immune cold cancer into one that responds to immunotherapy?
Analysis Reveals How Kidney Cancer Develops and Responds to Treatment
June 10, 2021 / MctpNot all kidney cancers behave the same, with wildly different responses to immunotherapy or other treatments – and wildly different outcomes for patients as a result. By sequencing the RNA of individual cells within multiple benign and cancerous kidney tumors, researchers from the University of Michigan Rogel Cancer Center have identified the cells [...]
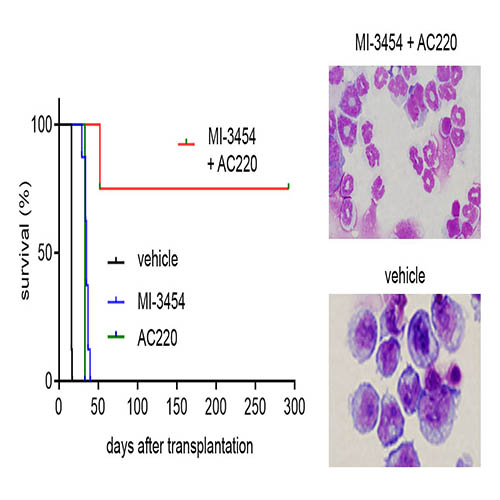
Researchers Develop First-in-Class Inhibitors Against Key Leukemia Protein
May 17, 2021 / CancerA research effort by Drs. Jolanta Grembecka and Tomasz Cierpicki was just published in Nature Communications. Learn more about the protein made by the ASH1L gene, which plays a key role in the development of acute leukemia, along with other diseases [...]
Study Suggests Path to Blocking Common Genetic Driver of Lung Cancer
May 12, 2021 / MctpStopping the interaction between KRAS and the protein AGO2 slowed tumor growth in mouse models.
Biomarker Could Help Identify Difficult-to-Diagnose Kidney Cancer Subtype
April 14, 2021 / Cancer ResearchMiTF renal cell carcinoma can masquerade as other subtypes and may not respond as well to front-line therapies.
Study Explains Why Patients with Cancer Spread to the Liver Have Worse Outcomes
January 5, 2021 / CancerA new study by the University of Michigan's Rogel Cancer Center analyzed patients with cancer and the factors that cause the cancer to spread to the liver, leading to worse outcomes.
Prostate Cancer Regulator Plays Role in COVID-19, Providing a Promising Treatment Lead
December 22, 2020 / Cancer ResearchClinical trials underway are testing whether drugs that target the androgen receptor – successful in controlling prostate cancer – could also work against the coronavirus. wo proteins, ACE2 and TMPRSS2, help the coronavirus gain entry and replicate within cells. TMPRSS2 is well-known to Arul Chinnaiyan, MD, PhD. His lab discovered that TMPRSS2 fuses with the ETS gene to drive more than half of all prostate cancers [...]
Research Led by Drs. Cierpicki and Grembecka Published in "Blood"
December 2, 2020 / CancerA new study led by Drs. Jolanta Grembecka and Tomasz Cierpicki of the Department of Pathology was just published in Blood's American Society of Hematology. The research focuses on combinatorial treatment with menin and FLT3 and how inhibitors induce complete remission in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) with activating FLT3 mutations [...]
Dr. Celina Kleer Wins ASIP 2020 Outstanding Investigator Award
November 12, 2020 / AsipCongratulations to Dr. Celina Kleer who was awarded the American Society for Investigative Pathology (ASIP)'s 2020 Outstanding Investigator Award. Dr. Kleer receives the award for her demonstrated excellence in research in experimental pathology [...]
Scientists Develop First Drug-Like Compounds to Inhibit Elusive Cancer-Linked Enzymes
September 2, 2020 / Rogel Cancer CenterStructural biology techniques helped researchers target the nuclear receptor-binding SET domain family, whose malfunction is associated with several types of cancer.
Dr. Celina Kleer: Physician Scientist, Dedicated Mentor, ASIP Outstanding Investigator Awardee
July 20, 2020 / FacultyDr. Celina Kleer named 2019 AACR Outstanding Investigator in Breast Cancer Research
Dr. Udager Appears on '3Ps of Cancer' Podcast
July 14, 2020 / CancerDr. Aaron Udager recently appeared on Michigan Medicine's 3P's of Cancer: Prevention, Preparedness, Progress podcast
Diagnostic Biomarkers Uncovered for Rare Kidney Cancer
April 21, 2020 / Experimental PathologyResearchers have uncovered the gene signature for ChRCC.
Anti-Leukemia Compound Induces Complete Remission in Mouse Models
February 3, 2020 / Experimental PathologyA Phase I clinical trial, using a structurally related analog of the compound, is currently enrolling patients.
A Simple Twist of Cell Fate
January 15, 2020 / Experimental PathologyU-M researchers are shedding new light with exciting implications for research and health.
Kleer honored by the AACR
November 4, 2019 / Rogel Cancer CenterThe American Association for Cancer Research announced that Celina Kleer, MD, the Harold A. Oberman Collegiate Professor of Pathology and Director of the Breast Pathology Program, will be the recipient of the 2019 Outstanding Investigator in Breast Cancer Research, supported by the Breast Cancer Research Foundation.

















 ON THE COVER
ON THE COVER
 ON THE COVER
ON THE COVER
 ON THE COVER
ON THE COVER
 ON THE COVER
ON THE COVER
 ON THE COVER
ON THE COVER
 ON THE COVER
ON THE COVER
 ON THE COVER
ON THE COVER
 ON THE COVER
ON THE COVER
 ON THE COVER
ON THE COVER
 ON THE COVER
ON THE COVER
 ON THE COVER
ON THE COVER
